Composition and abundance of decapod crustaceans in mixed seagrass meadows in the Paraguaná Peninsula, Venezuela
Abstract
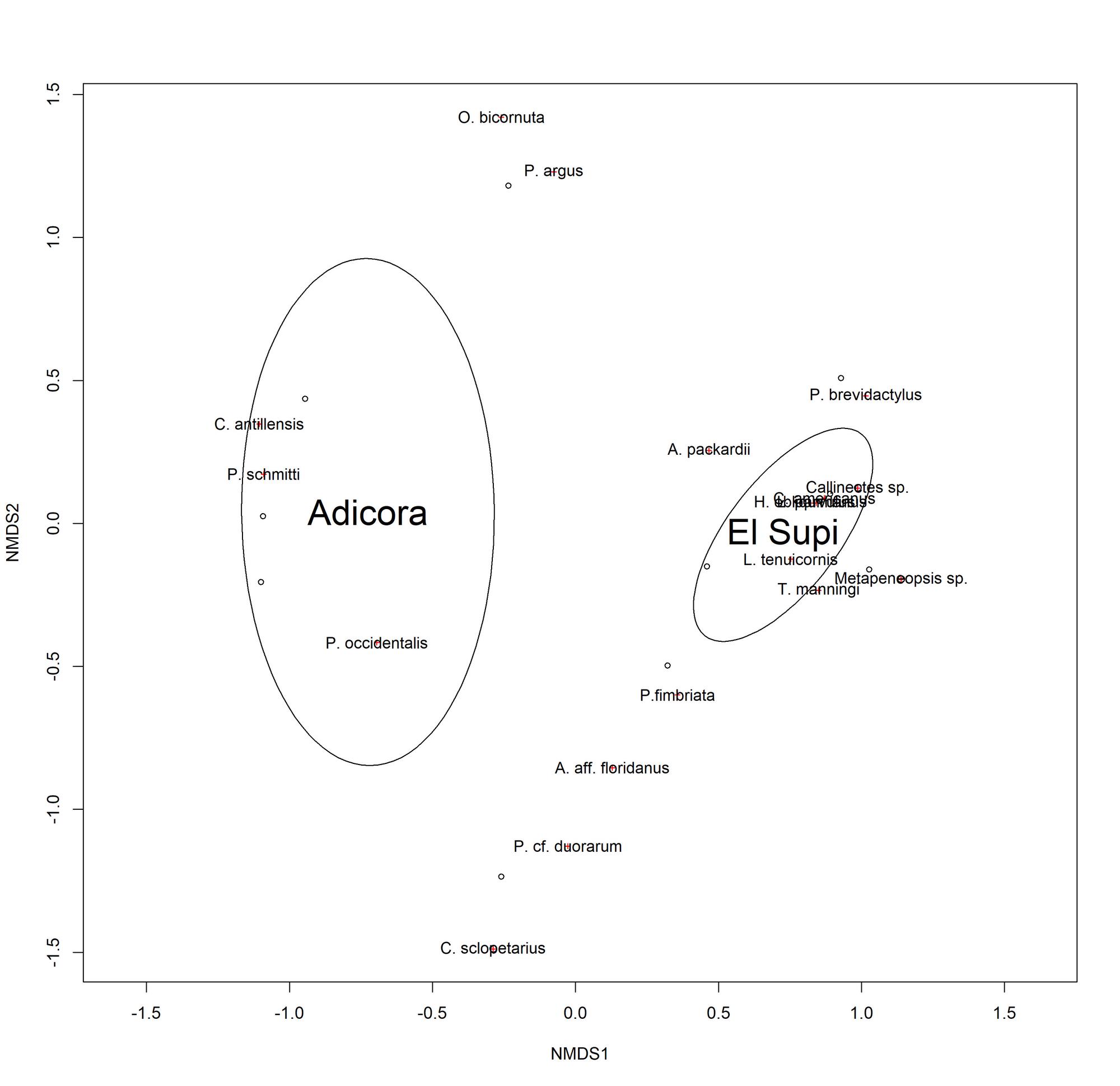
Thalassia testudinum and Halodule wrigthii are the dominant seagrasses in the Caribbean, being common across shallow shorelines, either as monospecific or as intermixed meadows. Among the macrofauna associated with these beds, crustaceans are considered essential for the whole ecosystem functioning. However, knowledge about the associated community of decapod crustaceans in assemblages of T. testudinum and H. wrigthii is still scarce, particularly outside of protected areas. Here we report eight new decapod species for the Paraguaná Peninsula (Falcón State, Venezuela) in association with intermixed seagrass beds: Achelous tumidulus Stimpson, 1871, Alpheus aff. floridanus Kingsley, 1878, Chorinus heros (Herbst, 1790), Clibanarius antillensis (Stimpson, 1859), Clibanarius sclopetarius (Herbst, 1796), Latreutes parvulus (Stimpson, 1866), Panopeus occidentalis Saussure, 1857, and Processa fimbriata Manning & Chace, 1971. These records represent habitat extensions and fill gaps in the geographical distribution of the species along the northern coast of South America. Furthermore, we found that statistical differences in decapod species abundance and composition are likely to be caused by the joint action of coverage and heterogeneity of the beds. Our results indicate that typical Caribbean species were the most influential in the community; nevertheless, the abundance of juvenile Penaeus schmitti Burkenroad, 1936 was notable, since they have rarely been found in these habitats. This finding highlights the role of non-protected areas as nursery habitats for economically important species. Our results show that seagrass meadows in the Paraguaná Peninsula reflect overall good health when compared to other Caribbean zones, representing an important habitat for the maintenance of crustacean populations.